5 benefits to an IT automation mindset
Article by Supannee Amnajmongkol, Red Hat Thailand Country Manager
IT automation has become one of the dominant factors that fosters success in the tech industry, and can be a game-changer for anyone looking to streamline their IT operations.
What is IT automation?
To put it simply, IT automation is all about using software to handle those repetitive administration tasks we usually do manually. Think of it like setting up a bunch of smart routines that take care of things for you, helping your IT environment run smoothly and scale quickly when needed.
What are the advantages of IT automation?
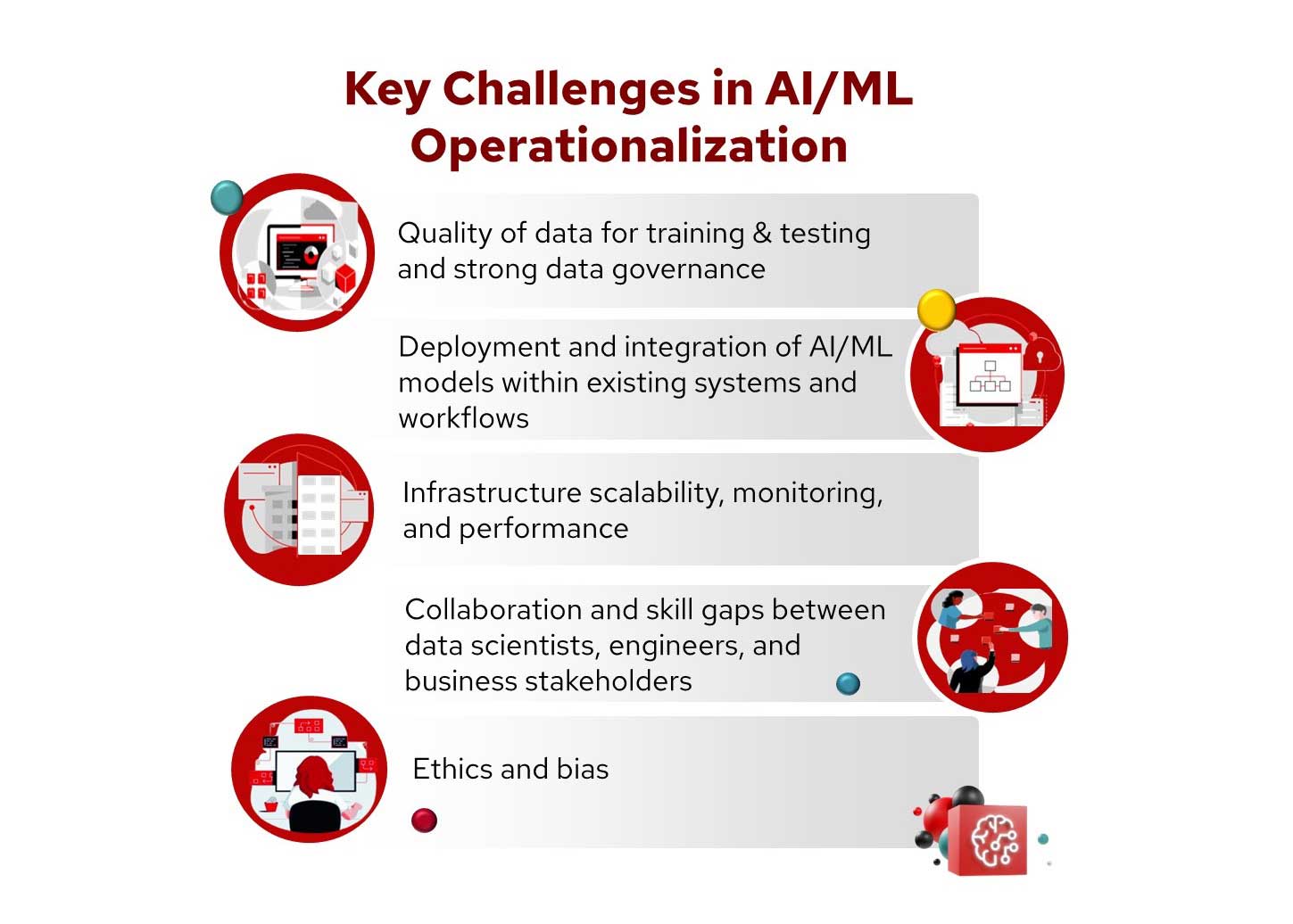
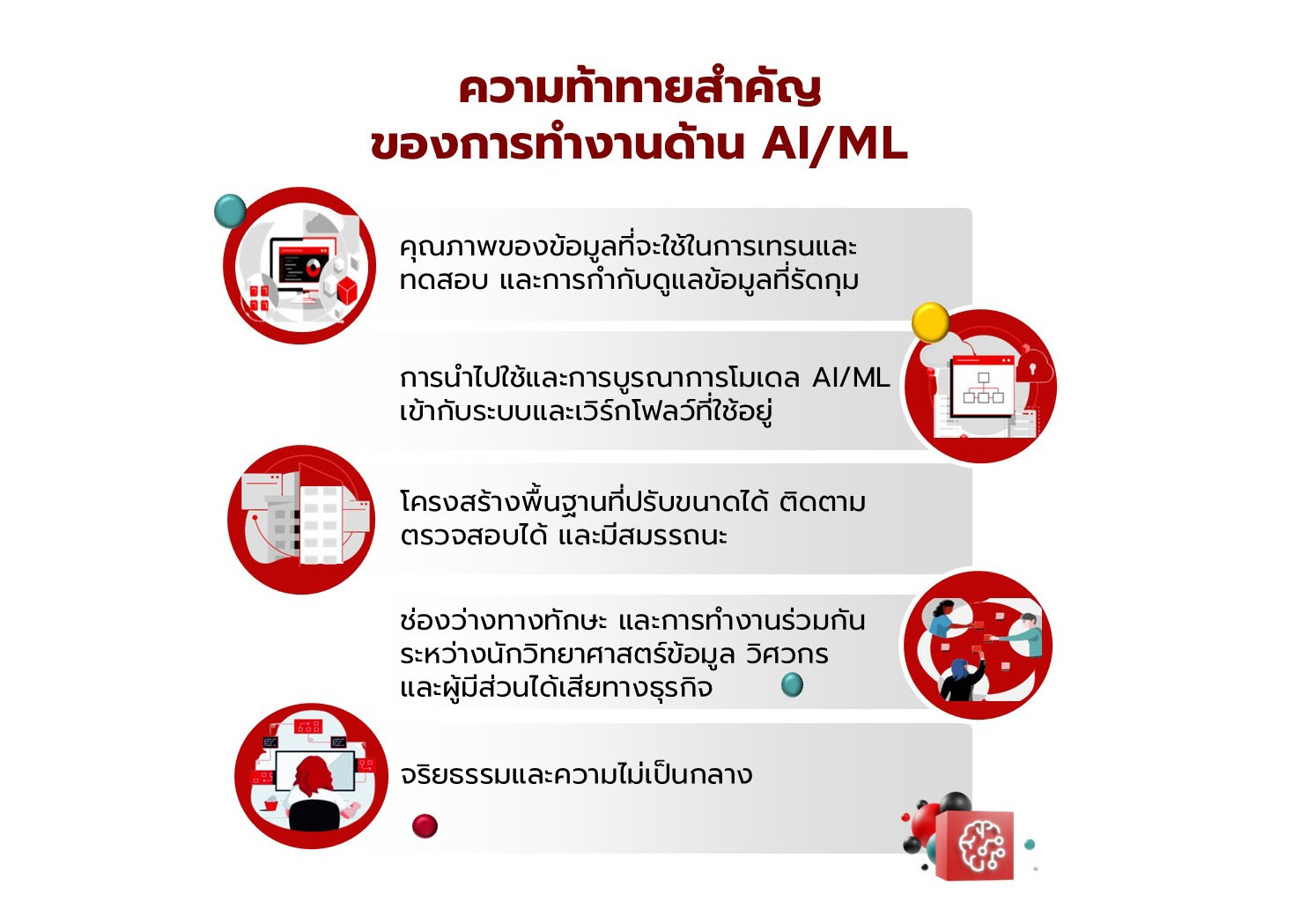
Incorporating automation into your IT process comes with a bunch of benefits. It’s not just about making things more efficient, it’s about enabling a more secure, innovative and flexible work environment. Here are 5 benefits why adopting an IT automation mindset can boost your IT operations in your organization:
- Streamlines IT operations to create space for innovation
Automation can take over many complicated IT tasks, reducing the need for constant intervention and clearing up those pesky bottlenecks. This means your systems can run more reliably and your processes will be more efficient.
By reducing the number of repetitive tasks your IT team has to manage on a daily basis, automation gives them the time and freedom to think more creatively and take on new, exciting projects. This helps create an environment that fosters continuous improvement and innovation.
- Improves accuracy and reduce errors
Automated processes are less likely to be subject to human error, and will therefore be completed to a much higher standard of accuracy than any human-dependent procedure. This means you can expect tasks to be done with fewer costly mistakes.
- Accelerates time-to-market
Automation can help increase team productivity and make development and deployment phases faster and more flexible. This helps you get your products and services to market quicker, giving you a competitive advantage.
With automation, you can gather and rapidly analyze large volumes of data, which comes in handy for making smart decisions and strategic planning.
- Strengthens security posture and compliance
Automation can help improve your IT security posture by simplifying the implementation of consistent security policies and compliance measures. For customers like Cepsa, automation allows them to save time and focus on the processes that help with compliance and cyber security. Automation helps make systems more resilient and compliant through precise permission management and enforcement of robust security protocols.
- Enhances disaster recovery and business continuity
Imagine your main computer crashes or loses all its data. Disaster recovery is about having a plan to quickly restore your IT systems and data after such a major event, while business continuity means that your essential operations are able to keep running smoothly, no matter what happens. Automated routines for backup and recovery make this process a lot simpler and more reliable.
For example, if you experience a catastrophic system failure, automated processes help restore critical data and system files quickly and reliably. This reduces potential downtime and helps your business maintain routine operations even in times of major disruption.
Automating IT tasks isn’t just about making work more efficient—it can also represent a fundamental shift in organizational strategy. Today’s companies – no matter what industry – need to be flexible and sustainable. Automation can help organizations become more innovative and efficient, while also boosting their overall security posture. It can help organizations become more responsive, too—proactively embracing IT automation is one way tech companies can increase their agility and remain ready for future challenges.
No matter the complexity of your environment or where you are on your IT modernization journey, an IT operations automation strategy can help you improve existing processes. With automation, you can save time, increase quality, improve employee satisfaction and reduce costs throughout your organization.